Always, AC motors have been one of the focuses of everyone’s attention. Therefore, in view of everyone’s interest, the editor will bring you the relevant introduction of AC motors. Please see the following for details.
- Common faults and solutions of AC motors
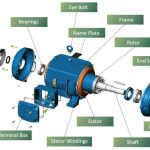
“AC motor” is a machine used to realize the mutual conversion of mechanical energy and AC power. Due to the huge development of AC power systems, AC motors have become the most commonly used motors. Compared with DC motors, AC motors have no commutator (see commutation of DC motors), so they have simple structure, convenient manufacturing, relatively strong, and easy to make high-speed, high-voltage, high-current, and large-capacity motors. The power coverage of AC motors is very large, ranging from a few watts to hundreds of thousands of kilowatts, or even millions of kilowatts. In the early 1980s, the largest steam turbine generator had reached 1.5 million kilowatts.
AC motors are a common type of equipment used in industrial production. Common faults include the following:
- The motor is difficult to start, and the speed suddenly changes or becomes unstable after starting: This fault may be caused by unstable power supply voltage, wrong connection of the three-phase circuit of the motor, poor contact of the stator winding, eccentric wear of the rotor, bearing damage, etc.
- The motor makes abnormal noise: Motor bearing failure, eccentric wear of the rotor, looseness of the stator, wear of the gear transmission, or non-vertical output shaft may all cause abnormal noise in the motor.
- Abnormal heat problems in the motor: It may be caused by motor fan failure, too tight or too loose bearings, too high temperature of the stator or rotor windings, etc.
- Line break or short circuit: Line break or short circuit caused by aging, breakage or poor connection, or short circuit to the ground can easily cause the motor to burn out.
- Bearing failure: Bearing failure caused by aging, poor lubrication, or too tight or too loose bearings, which will increase motor noise and rotation resistance, and in severe cases, cause the motor to stop.
The above are some common faults of AC motors, which require regular maintenance and inspection, timely troubleshooting, ensuring the normal operation of the motor and extending the service life of the motor.
Solutions to AC motor faults:
- Check the power supply: If you find that the motor is not running, you need to check the power supply first. Make sure that the power required by the motor has been started. If the power supply is not started, the motor cannot work properly.
- Check the motor circuit: Check the motor circuit. Make sure that the motor wires and sockets are not damaged or loose. Is the power switch turned on.
- Check the motor capacitor: The motor capacitor is prone to failure after long-term use. Check whether the capacitor is operating normally.
- Check the motor bearing: Lack of oil or wear of the bearing will also affect the operation of the motor. The bearing needs to be lubricated or replaced.
- Check the motor fan: If the motor cooling fan is damaged or blocked, it will also affect the operation of the motor. The motor fan needs to be cleaned to ensure its normal operation.
- Check the motor rotor: Check whether the motor rotor is damaged, deformed, etc. If so, the motor rotor needs to be replaced.
- Check the motor stator winding: The motor stator winding may be damaged due to short circuit, poor contact and other reasons. Professional maintenance personnel are required to inspect and repair it.
If no problem is found in the above steps, it may be a comprehensive motor failure. The entire system needs to be inspected and maintained.
When replacing the winding, the original winding form, size, number of turns, wire gauge, etc. must be recorded. When these data are lost, they should be obtained from the manufacturer. The original design winding is changed at will, which often deteriorates one or several performances of the motor, or even makes it unusable.
How to maintain and maintain AC motors
The use environment should always be kept dry, the motor surface should be kept clean, and the air inlet should not be blocked by dust, fibers, etc.
When the thermal protection of the motor is continuously activated, it should be found out whether the fault comes from the motor or the overload or the setting value of the protection device is too low. After eliminating the fault, it can be put into operation.
The motor should be well lubricated during operation. Generally, the motor should be replenished or replaced with grease after running for about 5,000 hours. When the bearing is found to be overheated or the lubrication is deteriorated during operation, the hydraulic grease should be replaced in time. When replacing the grease, the old lubricating oil should be removed, and the oil grooves of the bearings and bearing covers should be cleaned with gasoline, and then ZL-3 lithium-based grease should be filled into 1/2 (for 2 poles) and 2/3 (for 4, 6, and 8 poles) of the cavity between the inner and outer rings of the bearing.
When the life of the bearing ends, the vibration and noise of the motor operation will increase significantly. When the radial clearance of the bearing reaches the following values, the bearing should be replaced.
When disassembling the motor, the rotor can be taken out from the shaft extension end or the non-extension end. If it is not necessary to remove the fan, it is more convenient to take out the rotor from the non-extension end. When pulling the rotor out of the stator, damage to the stator winding or insulation should be avoided.