How to test electric motor top speed?
The Basics of Motor Speed
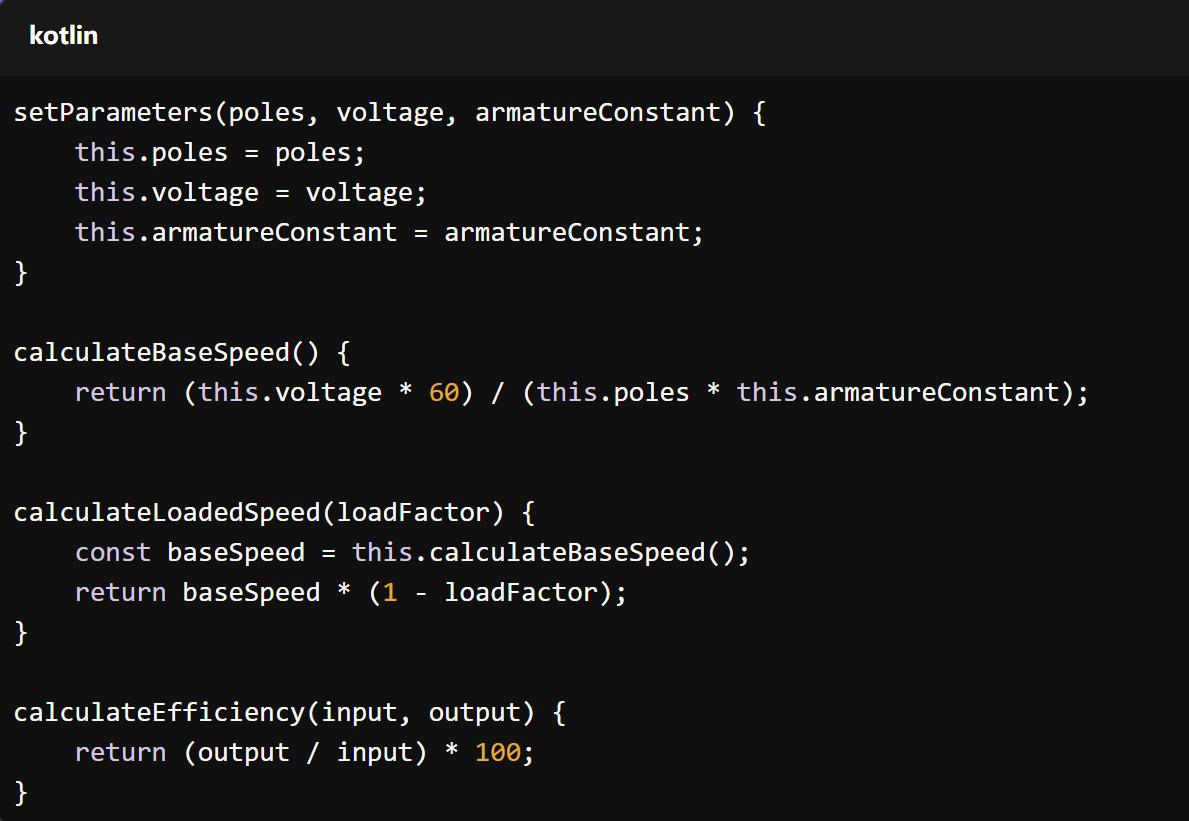
Think of motor speed like a simple math problem. Here’s the basic formula:
Speed = (Voltage × 60) / (Poles × Motor Constant)
In everyday terms:
- Speed: How fast the motor spins (in RPM – rounds per minute)
- Voltage: The electrical power you put in
- Poles: Parts inside the motor that make it turn
- Motor Constant: A number that depends on how the motor is built
What Affects Motor Speed?
- Power Supply
- How much voltage you use
- How steady the power is
- Whether the power stays constant
- Motor Design
- How the motor is built inside
- What materials it uses
- How many magnetic parts it has
- Load (What the Motor is Moving)
- How heavy the load is
- How much resistance there is
- What the motor is trying to do
Different Types of Speed
No-Load Speed
This is like your motor running free – nothing attached:
- Fastest possible speed
- No weight or resistance
- Perfect conditions
- Used for testing
Normal Working Speed
The speed when the motor is doing its job:
- Regular operating speed
- What the manufacturer recommends
- Speed with normal load
- Everyday use speed
Real-World Speed
What actually happens when you use it:
- Varies based on conditions
- Changes with different loads
- Affected by temperature
- Depends on how you use it
Practical Uses
In Factories
- Running machines
- Moving materials
- Powering tools
- Operating equipment
In Transportation
- Electric cars
- Trains
- Boats
- Airplanes
In Special Equipment
- Medical devices
- Lab equipment
- Precision tools
- Research machines
Taking Care of Your Motor
Regular Maintenance
- Check for wear and tear
- Keep it clean
- Watch for unusual sounds
- Monitor temperature
Efficient Operation
- Don’t overload it
- Keep it cool
- Use the right power
- Follow the manual
When to Get Help
- Unusual noises
- Getting too hot
- Not running smoothly
- Performance drops
Remember: A well-maintained motor lasts longer and runs better. If you’re not sure about something, it’s always best to ask an expert!