How does an electric motor work?
The application occasions of motors are very wide, covering many fields such as industry, household appliances, transportation, etc.
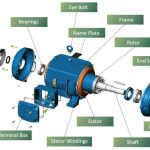
The Basic Parts
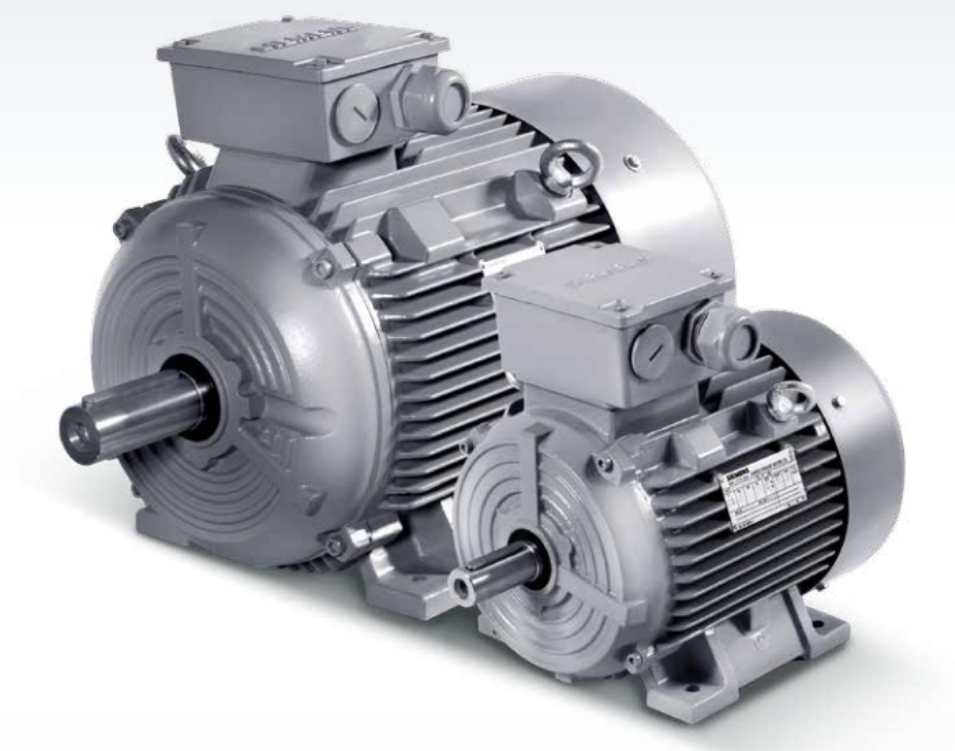
All electric motors have two key things. One is called the stator – it makes a magnetic field but doesn’t move. The other is the rotor – it spins due to the stator’s field. Motors also need power, like batteries or wall plugs, to supply electricity.
Inside Details
Copper wire is coiled tightly around the stator. When power flows, these coils create a magnetic pull. Magnets in the rotor feel this pull. Their attraction and pushing makes the rotor spin smoothly inside. Slip rings or brushes keep the current moving to the always-spinning rotor.
Different Types
Motors come in varieties. Some work great in factories. Others sync up precisely. Some let you control speed. Others move in tiny steps for robots. New kinds are efficient for electric cars too.
How It All Works
Electricity energizes the stator coils, making magnetic fields. These fields grasp the rotor magnets and get them spinning. As the rotor rotates, the fields keep it going round and round the stator. The attached shaft then uses this spin to power things outside. Electric motors connect electricity to mechanics in amazing ways!